In this intriguing article, we will uncover the intricate connections between women’s mental health and chronic physical health conditions. Delving into this fascinating topic, we will explore the powerful linkages that exist between these two aspects of a woman’s overall well-being. By understanding the complex interplay between mental and physical health, we can gain valuable insights into how to support and empower women to maintain a holistic sense of wellness. So, grab a cup of tea, settle in, and join us on this enlightening journey through the connections between women’s mental health and chronic physical health conditions.
Understanding Women’s Mental Health
The impact of mental health on overall well-being
Women’s mental health is of utmost importance as it directly affects their overall well-being. Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, and it plays a significant role in how women perceive themselves, their abilities, and their capacity to cope with life’s challenges. When a woman’s mental health is compromised, it can impact various aspects of her life, including her relationships, career, and physical health. Therefore, it is crucial to understand and address women’s mental health needs for the sake of their overall well-being.
Common mental health conditions in women
In the realm of mental health, there are several conditions that women are more prone to experiencing compared to men. Some of the most common mental health conditions in women include depression, anxiety disorders, eating disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These conditions can manifest differently in women and may be influenced by a range of factors, such as hormonal changes, reproductive health issues, and societal expectations. Recognizing these conditions and providing appropriate support and treatment is essential in promoting women’s mental health and well-being.
Gender differences in mental health
While men and women can both experience mental health conditions, it is important to acknowledge the gender differences that exist. Women tend to be more vulnerable to certain mental health issues, including depression and anxiety disorders. This can be attributed to various factors, such as hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause. Additionally, women may face unique stressors and societal pressures that can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health conditions. Understanding these gender differences is crucial in tailoring effective interventions and support systems for women’s mental health.
Types of Chronic Physical Health Conditions
The prevalence of chronic physical health conditions in women
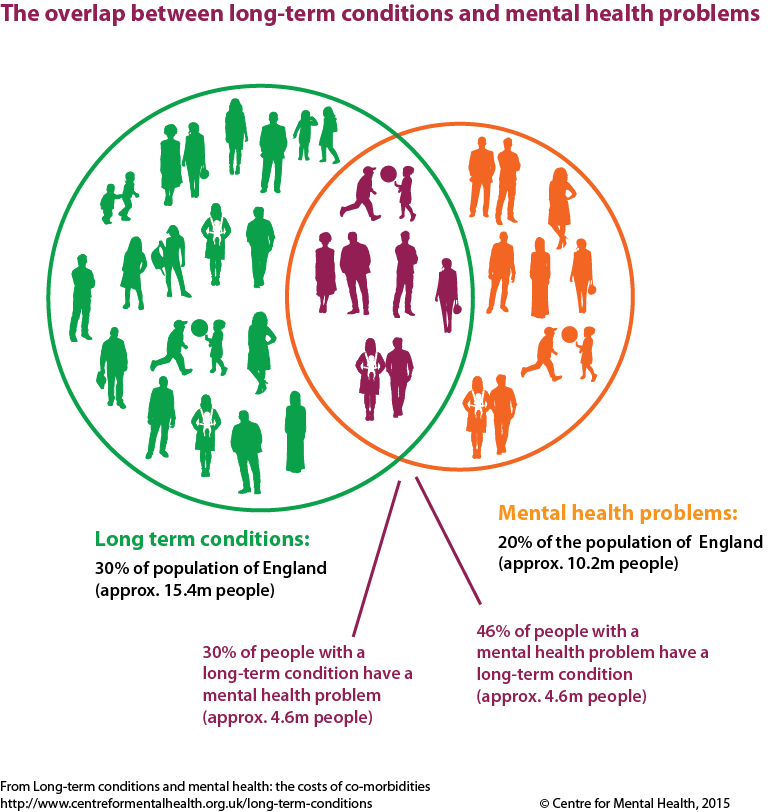
In addition to mental health, women also face a significant burden of chronic physical health conditions. Chronic physical health conditions are defined as long-term medical conditions that require ongoing management and care. These conditions can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life and may include conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and chronic pain disorders. Women’s higher susceptibility to certain chronic physical health conditions highlights the need for gender-specific approaches to prevention, diagnosis, and management.
Examples of chronic physical health conditions commonly experienced by women
There are various chronic physical health conditions that are more prevalent in women. For instance, autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis tend to affect women more frequently. Hormonal factors, genetic predispositions, and immune system differences contribute to this gender disparity. Additionally, conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and fibromyalgia significantly impact the well-being of many women. Addressing these chronic physical health conditions is essential in improving women’s overall health and reducing their risk for mental health complications.
The Bidirectional Relationship Between Women’s Mental Health and Chronic Physical Health Conditions
The impact of chronic physical health conditions on mental health
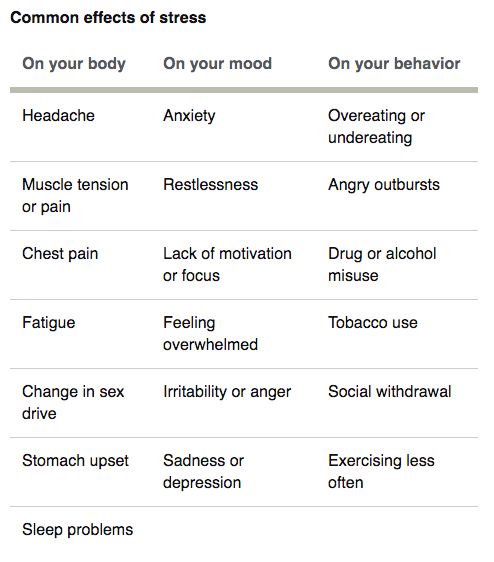
When women experience chronic physical health conditions, their mental health can be significantly affected. The burden of managing a chronic condition, dealing with physical pain or limitations, and facing potential lifestyle changes can lead to feelings of stress, anxiety, and depression. Moreover, the emotional toll of having to deal with a long-term health condition can exacerbate symptoms of pre-existing mental health conditions or result in the development of new ones. It is therefore crucial to provide comprehensive support that addresses both the physical and mental aspects of women’s health when managing chronic conditions.
The impact of mental health on the development and management of chronic physical health conditions
Conversely, women’s mental health has a notable impact on the development and management of chronic physical health conditions. A woman’s mental state can affect her ability to cope with her condition, adhere to treatment plans, and make necessary lifestyle changes. Depression, for example, may lead to noncompliance with medication regimens or self-care practices, which can negatively impact the management of chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease. Recognizing and addressing women’s mental health needs within the context of chronic physical health conditions is essential for optimizing health outcomes.
Risk Factors for Women’s Mental Health and Chronic Physical Health Conditions
Socioeconomic factors
Various socioeconomic factors can contribute to both women’s mental health issues and the development of chronic physical health conditions. Women who face financial instability, lack access to education and employment opportunities, or experience discrimination may be at a higher risk for mental health problems. Similarly, socioeconomic disparities can limit women’s access to healthcare, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment of chronic physical health conditions. Addressing these disparities through policies and interventions that promote financial security, education, and equal opportunities is essential for improving women’s mental and physical health outcomes.
Genetic and biological factors
Genetic and biological factors also play a role in women’s mental and physical health. Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause can contribute to the development of mental health conditions in women. Additionally, certain genetic predispositions may increase a woman’s susceptibility to both mental health issues and chronic physical health conditions. Understanding the genetic and biological factors that influence women’s health can inform personalized approaches to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Lifestyle factors
Lifestyle factors, including diet, physical activity, and substance use, can have a significant impact on women’s mental and physical health. Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition, and excessive alcohol or tobacco use, can increase the risk of developing chronic physical health conditions and exacerbate mental health issues. Promoting healthy lifestyle choices through education, community programs, and accessible resources is crucial to reducing the burden of both mental and physical health conditions in women.
Barriers to Diagnosis and Treatment of Women’s Mental Health and Chronic Physical Health Conditions
Gender bias in healthcare
Gender bias in healthcare can be a significant barrier to the accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of women’s mental health and chronic physical health conditions. Historically, women’s medical concerns have often been dismissed or not taken seriously, leading to delayed or incorrect diagnoses. This bias can harm women’s mental and physical well-being and undermine their confidence in seeking timely healthcare. It is important for healthcare professionals to be aware of and address any biases to ensure equitable access to diagnosis and treatment for women.
Stigma surrounding mental health
The stigma surrounding mental health remains a major barrier to women seeking help and support for their mental well-being. Many women may fear being labeled or judged if they openly discuss their mental health struggles. This stigma can prevent women from seeking professional help, leading to delays in diagnosis and treatment. Creating a supportive and nonjudgmental environment where women feel comfortable discussing their mental health is crucial in breaking down this barrier and promoting early intervention and effective treatment.
Access to healthcare and insurance coverage
Limited access to healthcare and lack of insurance coverage can significantly impede women’s ability to seek proper diagnosis and treatment for both mental health conditions and chronic physical health conditions. Women who lack financial resources or adequate insurance coverage may struggle to afford necessary medications, therapies, or regular check-ups. This can negatively impact their overall health outcomes and exacerbate both mental and physical health conditions. Addressing these access barriers through affordable healthcare options and insurance reforms is essential for ensuring women receive the care they need.
Effective Strategies for Managing Women’s Mental Health and Chronic Physical Health Conditions
Integrative healthcare approaches
Integrative healthcare approaches that consider both the mental and physical aspects of women’s health can be highly effective in managing mental health conditions alongside chronic physical health conditions. This may involve collaborative care from healthcare professionals, including psychologists, psychiatrists, and primary care providers who work together to address both mental and physical needs. Integrative approaches can help women develop comprehensive treatment plans that cater to their specific circumstances, increase adherence to treatment, and improve overall health outcomes.
Psychotherapy and counseling
Psychotherapy and counseling are essential components of managing women’s mental health conditions and their impact on chronic physical health conditions. Therapeutic interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or interpersonal therapy, can empower women to develop healthy coping mechanisms, improve their emotional well-being, and enhance their overall quality of life. Therapists and counselors can also assist women in navigating the challenges associated with chronic physical health conditions, helping them find resilience and support in their journey to wellness.
Support groups and peer support
Support groups and peer support can play a crucial role in women’s mental health and the management of chronic physical health conditions. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide a sense of belonging, validation, and understanding. These support networks can offer women opportunities to share their struggles, gain insights, and receive advice from their peers. Support groups can significantly reduce feelings of isolation and provide invaluable emotional support for women navigating the complexities of mental and physical health challenges.
Self-care practices
Prioritizing self-care is vital for managing women’s mental and physical health conditions. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation, stress reduction, and overall well-being can significantly contribute to mental and physical health outcomes. Self-care practices may include regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, getting sufficient sleep, practicing mindfulness or meditation, engaging in hobbies, and setting boundaries to manage stress. By incorporating self-care into their daily routines, women can better cope with their mental and physical health challenges and cultivate a positive and empowering relationship with themselves.
The Importance of Holistic Care for Women’s Mental and Physical Health
Recognizing the interconnectedness of mental and physical health
Recognizing the interconnectedness of mental and physical health is crucial for providing holistic care to women. Mental and physical health are intertwined, and addressing one without considering the other can lead to suboptimal outcomes. Women’s mental well-being impacts their ability to manage and cope with chronic physical health conditions, and vice versa. By adopting a holistic approach that acknowledges this interplay, healthcare providers can offer comprehensive and person-centered care that addresses the unique needs of each woman.
The role of healthcare providers in promoting holistic care
Healthcare providers play a vital role in promoting holistic care for women’s mental and physical health. By adopting a patient-centered approach, healthcare providers can create a supportive and inclusive environment where women feel comfortable discussing their mental health concerns in addition to their physical symptoms. This requires open communication, active listening, and a commitment to addressing the multidimensional needs of each woman. Healthcare providers can also collaborate with other professionals, such as mental health specialists and social workers, to ensure comprehensive care and optimal outcomes for women.
Creating a supportive environment for women’s health
Creating a supportive environment for women’s health involves addressing societal and cultural factors that can hinder access to care and perpetuate stigma. It requires promoting gender equity, challenging gender biases in healthcare, and advocating for policies that prioritize women’s mental and physical well-being. Additionally, creating safe spaces for women to discuss their mental health and physical concerns can help combat stigma and encourage early intervention. Empowering women through education, awareness campaigns, and community initiatives can foster a supportive environment that values and prioritizes women’s holistic health.
Research and Policy Implications
Promoting interdisciplinary research
Interdisciplinary research is essential for gaining a comprehensive understanding of the links between women’s mental and physical health. Collaborative studies involving researchers from various fields, such as psychology, medicine, sociology, and public health, can shed light on the complex interplay between mental health and chronic physical health conditions in women. By prioritizing interdisciplinary research, we can uncover new insights, develop effective interventions, and inform policy decisions that improve women’s health outcomes.
Addressing gender disparities in healthcare
Gender disparities in healthcare must be actively addressed to ensure equitable access to diagnosis, treatment, and management of mental and physical health conditions for women. This includes addressing biases in healthcare settings, promoting gender-sensitive care, and involving women in the decision-making processes regarding their health. Policymakers can work towards eliminating gender-related gaps in healthcare access, affordability, and quality of care. By prioritizing gender equity, we can eliminate barriers and ensure that women receive the care they need to achieve optimal mental and physical health.
Improving access to mental healthcare and chronic disease management
Improving access to mental healthcare and chronic disease management is vital to enhancing women’s health outcomes. This includes increasing the availability and affordability of mental health services, integrating mental health care into primary healthcare settings, and expanding insurance coverage for mental health conditions. Similarly, enhancing access to chronic disease management programs, ensuring medication affordability, and promoting lifestyle interventions can empower women to effectively manage their chronic physical health conditions. By addressing access barriers, we can promote early intervention and support for the holistic well-being of women.
Conclusion
Women’s mental and physical health are intricately connected, and addressing one without considering the other can lead to suboptimal outcomes. Understanding the links between women’s mental health and chronic physical health conditions is crucial for providing comprehensive care that improves overall well-being. By recognizing the impact of mental health on women’s ability to manage chronic physical health conditions and vice versa, healthcare providers, policymakers, and society as a whole can work together to promote the holistic health of women. Through interdisciplinary research, addressing barriers, and prioritizing women’s mental and physical health, we can create a future where women receive the support and care they need to thrive.