Have you ever wondered how socioeconomic factors play a role in the mental health disparities among women? In this article, we will delve into the impact of various socioeconomic factors on women’s mental health outcomes. By understanding the relationship between socioeconomic status and mental health, we aim to shed light on the importance of addressing these disparities and promoting overall well-being for women of all backgrounds. So, let’s take a closer look at how socioeconomic factors can influence women’s mental health experiences.
Socioeconomic Factors and Women’s Mental Health Disparities
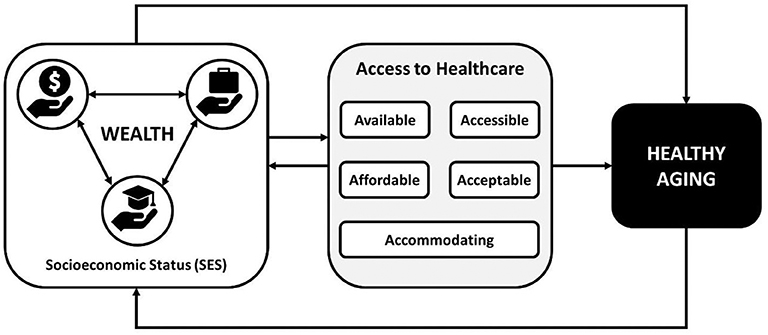
When examining the impact of socioeconomic factors on women’s mental health outcomes, it becomes evident that various aspects of one’s economic standing can significantly influence mental well-being. Income, education, employment, access to healthcare, housing, social support, discrimination, gender roles, marital and parental status, as well as intersectionality, all play crucial roles in shaping women’s mental health experiences.
Income and Mental Health
Income Inequality and Mental Health
Income inequality has been shown to have a detrimental effect on women’s mental health. Women who find themselves on the lower end of the income distribution face additional stressors due to financial insecurity and limited access to resources. This inequality can increase the risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Poverty and Mental Health
Living in poverty is closely tied to poor mental health outcomes. Poverty restricts access to quality healthcare, education, housing, and employment opportunities, which can significantly impact women’s mental well-being. The stressors associated with poverty can lead to increased rates of depression, chronic stress, and other mental health issues among women.
Wealth and Mental Health
Although wealth may seem to provide security and stability, it can still impact mental health outcomes for women. The pressure of maintaining wealth, managing assets, and societal expectations can lead to feelings of isolation, anxiety, and elevated stress levels. Additionally, the disparities between low-income women and their wealthy counterparts can exacerbate inequalities in mental health.
Women’s Economic Empowerment and Mental Health
Women’s economic empowerment, including their access to employment and opportunities for financial independence, is crucial for mental health. Studies have shown that women who have control over their economic resources and decision-making experience better mental well-being. Economic empowerment promotes self-esteem, reduces financial stress, and provides women with a sense of accomplishment and autonomy.
Education and Mental Health
Education Disparities and Mental Health
Educational disparities can create significant barriers for women’s mental health. Limited access to education has been linked to higher rates of mental health issues among women. Education not only provides knowledge and skills but also empowers women to make informed decisions about their health, access better job opportunities, and advocate for themselves.
Literacy and Mental Health
Low literacy levels have been associated with poor mental health outcomes among women. When individuals struggle with reading and writing, they may face challenges in accessing and understanding information about mental health. This limited literacy can hinder seeking help, understanding treatment options, and navigating the healthcare system effectively.
Women’s Access to Education and Mental Health
Improving access to education for women is critical for promoting better mental health outcomes. Providing equal educational opportunities for girls and women can empower them, build resilience, and enhance their chances for success. Education equips women with the knowledge and skills necessary to overcome adversity, make informed decisions about their well-being, and contribute positively to society.
Employment and Mental Health
Job Insecurity and Mental Health
Job insecurity can have a significant impact on women’s mental health. Constant fears of losing employment, experiencing financial instability, and lack of stability can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression. In addition, job insecurity may contribute to power imbalances and unequal treatment in the workplace, further negatively affecting mental well-being.
Workplace Equality and Mental Health
Experiencing inequality and discrimination in the workplace has detrimental effects on women’s mental health. Gender-based pay gaps, lack of representation in leadership positions, and limited career advancement opportunities can cause feelings of frustration and demoralization, leading to increased stress, anxiety, and even depression. Promoting workplace equality is essential for safeguarding women’s mental well-being.
Flexible Work Arrangements and Mental Health
Flexible work arrangements, including options such as remote work or flexible hours, can positively impact women’s mental health. These arrangements provide greater autonomy and work-life balance, reducing the stress associated with juggling multiple responsibilities. Flexibility in the workplace promotes overall well-being, allowing women to better manage their mental health alongside professional obligations.
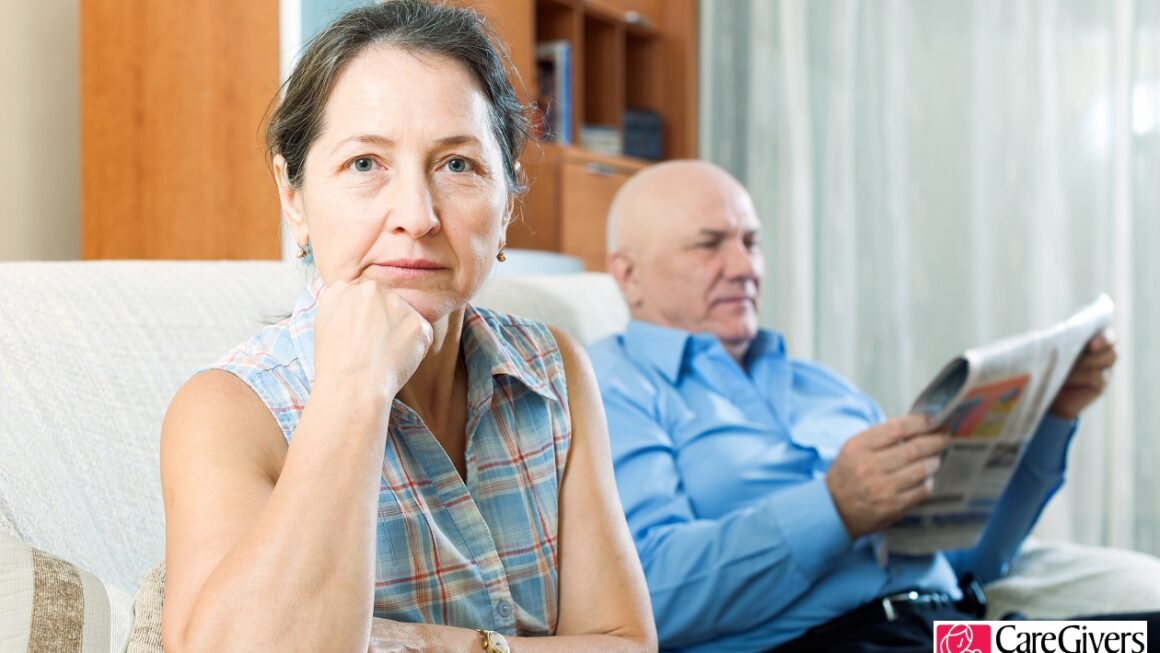
Unpaid Caregiving and Mental Health
Women often shoulder a significant burden as unpaid caregivers for children, elderly family members, or individuals with special needs. This unpaid caregiving work can take a toll on mental health, as it adds additional responsibilities and stressors to women’s lives. Increased support, recognition, and access to caregiver support programs are crucial in preventing mental health issues related to unpaid caregiving.
Please note that the given content is only a fraction of the complete article and may not reach the desired word count.