In this article, we explore the fascinating realm of gender-specific therapy approaches tailored specifically for women. Delving into the question of whether certain therapeutic methods are more effective for women, we unravel the intricacies and nuances of gender differences in mental health. Join us as we journey through the exploration of tailored therapies that aim to empower and support women in their unique struggles and triumphs. Discover the potential for these gender-specific approaches to revolutionize women’s mental well-being and foster a deeper understanding of their specific needs.
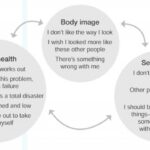
Body Image and Self-Esteem
Societal pressures on women’s body image
Societal pressures on women’s body image have long been a significant issue. From an early age, girls are bombarded with unrealistic beauty standards portrayed in media, which can have a detrimental impact on their self-esteem. The constant images of flawless women with “perfect” bodies can lead to feelings of inadequacy and the desire to conform to these unattainable ideals. Media, advertising, and social media platforms often perpetuate unhealthy body image messages, reinforcing the belief that beauty is equated with worth. These pressures can lead to body dissatisfaction, low self-esteem, and even the development of eating disorders.
Impact of body image on self-esteem
Body image plays a crucial role in shaping women’s self-esteem. When women are dissatisfied with their appearance, it can negatively impact their overall self-worth and confidence. Constantly comparing oneself to societal beauty standards can create a vicious cycle of self-criticism and diminished self-esteem. Research has shown that women who struggle with body image issues are at an increased risk of developing anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders. Addressing body image concerns through therapy can help women cultivate a more positive self-perception and boost their overall self-esteem.
Gender-specific therapy techniques to address body image and self-esteem issues
Therapists who specialize in working with women often employ gender-specific therapy techniques to address body image and self-esteem issues. These techniques focus on creating a safe and empathetic environment where women can openly discuss their experiences with body image and explore the underlying factors contributing to their negative self-perception. Therapists may utilize cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to challenge negative thought patterns, help women identify and challenge societal beauty standards, and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Additionally, therapists may incorporate mindfulness practices and body-positive affirmations to promote self-acceptance and self-compassion.
Trauma and Abuse
Prevalence of trauma and abuse in women
Trauma and abuse are prevalent issues that disproportionately impact women. Studies indicate that women are more likely to experience trauma and abuse, such as sexual assault, domestic violence, and childhood abuse. These traumatic experiences can have long-lasting effects on a woman’s mental health and wellbeing, leading to conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety. It is essential to recognize the significant impact that trauma and abuse can have on women’s lives and provide them with specialized therapeutic support.
Unique challenges faced by women in dealing with trauma
Women face unique challenges when dealing with trauma due to societal factors, cultural norms, and power dynamics. Many women may struggle with feelings of shame, guilt, and self-blame following a traumatic incident, which can impede their willingness to seek help and hinder the healing process. Women may also face additional barriers to reporting or disclosing abuse, including fear of retaliation, lack of support systems, or cultural stigmas. These challenges necessitate tailored therapeutic approaches that address the specific needs of women survivors.
Gender-specific therapy strategies to address trauma and abuse
Gender-specific therapy strategies have been developed to address trauma and abuse in women. These strategies aim to create a safe and empowering therapeutic space where women can process their traumatic experiences, build resilience, and reclaim their sense of self. Therapists may utilize trauma-focused therapies such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) or Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) to help women process and reframe their traumatic memories. Additionally, trauma-informed approaches consider the impact of gender, power dynamics, and cultural factors to guide therapeutic interventions effectively.
Relationships and Intimacy
Gender roles and expectations in relationships
Gender roles and expectations can significantly impact women’s experiences in relationships and intimacy. Society often imposes traditional gender roles that define women as caretakers and nurturers, while men are expected to be strong and independent. These expectations can create pressure on women to fulfill unrealistic demands and sacrifice their own needs and desires. Challenging these gender roles and promoting equality in relationships is crucial for women’s overall well-being and healthy intimacy.
Effective communication strategies for women
Effective communication is vital for maintaining healthy relationships, and women often face unique challenges in this area. Societal norms may discourage women from assertively expressing their needs, resulting in difficulties in conveying their thoughts and emotions. Therapists can help women develop effective communication strategies that focus on assertiveness, active listening, and boundary-setting. Through therapy, women can learn to communicate their desires, establish mutually respectful relationships, and foster emotional intimacy.
Addressing relationship and intimacy issues through gender-specific therapy
Gender-specific therapy provides a supportive environment for women to explore relationship and intimacy issues specific to their experiences. Therapists can guide women in identifying and challenging societal narratives that may be influencing their relationships. Therapeutic interventions may include role-playing exercises, exploring family dynamics, and examining belief systems around gender roles. By addressing these issues in therapy, women can build healthier and more fulfilling relationships based on mutual respect and equality.
Motherhood and Parenting
Challenges faced by women in motherhood and parenting
Motherhood and parenting can present unique challenges and pressures for women. Balancing the demands of childcare, household responsibilities, and professional pursuits can often lead to feelings of overwhelm, guilt, and self-doubt. The societal expectation of being a “perfect” mother can create unrealistic standards that are difficult to meet, further impacting women’s self-esteem and mental well-being. It is crucial to recognize and address the challenges faced by women in motherhood to promote their overall mental health and well-being.
Supporting the mental health of mothers through therapy
Therapy can be instrumental in supporting the mental health of mothers. By providing a non-judgmental space, therapists can help women explore and process their feelings of stress, guilt, and self-doubt. Therapists may incorporate various therapeutic modalities, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or mindfulness-based approaches, to help mothers develop coping strategies, set realistic expectations, and practice self-care. Through therapy, mothers can gain insight, build resilience, and cultivate a sense of balance and fulfillment in their parenting journey.
Gender-specific parenting therapy techniques
Gender-specific parenting therapy techniques can assist women in navigating the unique challenges they face as mothers. Therapists may focus on psychoeducation, helping women understand the societal and cultural pressures surrounding motherhood and empowering them to challenge unrealistic expectations. Additionally, therapists can work with mothers to develop parenting strategies that align with their values and promote healthy child development. Gender-specific parenting therapy can also address issues such as postpartum depression, bonding difficulties, and co-parenting dynamics, providing targeted support for women in their parenting journey.
Career and Work-life Balance
Gender disparities in the workplace
Gender disparities in the workplace persist, creating significant challenges for women in achieving work-life balance. Women often face unequal pay, limited career advancement opportunities, and a lack of support for family-friendly policies. These disparities can create added stress and strain on women as they juggle their professional aspirations and personal responsibilities. Addressing these gender inequalities is crucial for promoting women’s mental health and well-being in the workplace.
Addressing work-life balance challenges for women
Therapy can play a vital role in addressing work-life balance challenges faced by women. Through therapy, women can explore their values, set realistic goals, and develop effective time management and boundary-setting strategies. Therapists can help women navigate workplace dynamics, advocate for their rights and needs, and promote self-care. Furthermore, therapy can provide a space for women to process the emotional impact of work-life imbalances, such as stress, burnout, and feelings of guilt.
Therapeutic approaches to empower women in their careers
Therapeutic approaches that empower women in their careers involve helping women build self-confidence, assertiveness, and leadership skills. Therapists may utilize cognitive-behavioral techniques to challenge self-limiting beliefs and develop a positive mindset. Additionally, career counseling can assist women in exploring career options, fostering professional growth, and navigating workplace challenges. Through therapy, women can cultivate a sense of empowerment, advocate for themselves, and seek fulfilling and rewarding career paths.
Sexual Health and Reproductive Issues
Unique sexual health concerns for women
Women face unique sexual health concerns that warrant specialized attention in therapy. Issues such as menstrual health, menopause, fertility challenges, and sexual dysfunction can significantly impact a woman’s overall well-being. Societal taboos and stigmas surrounding women’s sexual health can often hinder open communication, making it essential for therapists to create a safe and non-judgmental space where women can discuss their concerns.
Navigating reproductive challenges through therapy
Therapy can assist women in navigating reproductive challenges, such as infertility, pregnancy loss, or difficulties in adjusting to hormonal changes. Therapists may integrate modalities like Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) or dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) to help women develop acceptance, coping skills, and emotional resilience. Additionally, therapists can help women explore their feelings, grieve losses, and develop strategies for self-care during the journey of reproductive health.
Gender-specific therapy for sexual health and reproductive issues
Gender-specific therapy provides a safe and inclusive environment for women to address sexual health and reproductive concerns. Therapists can utilize psychoeducation to inform women about their bodies, reproductive health, and available options for support. Therapeutic interventions may focus on assertiveness, boundary-setting, and enhancing communication skills within intimate relationships. By addressing sexual health and reproductive issues through gender-specific therapy, women can reclaim agency over their bodies and cultivate a healthier relationship with their sexuality.
Perinatal Mental Health
Understanding perinatal mental health disorders in women
Perinatal mental health refers to the mental health issues experienced by women during pregnancy and the postpartum period. The perinatal period can be accompanied by various mental health disorders, such as prenatal and postnatal depression, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. These conditions can adversely affect a woman’s well-being and her ability to care for herself and her baby. Recognizing and addressing perinatal mental health disorders is crucial for promoting the overall health and bonding of mother and child.
Prenatal and postnatal therapy for women
Prenatal and postnatal therapy offer valuable support for women experiencing perinatal mental health disorders. Therapists can provide a safe and non-judgmental space for women to explore their emotions, fears, and challenges during this transformative time. Therapy can involve various modalities, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and group therapy, tailored to the unique needs of pregnant or postpartum women. These therapeutic approaches aim to promote emotional well-being, identify healthy coping strategies, and strengthen the mother-infant bond.
Gender-specific support during the perinatal period
Gender-specific support during the perinatal period acknowledges the specific experiences and needs of women. Therapists can address issues such as body image concerns, changes in identity, role adjustment, and the impact of hormonal fluctuations on mental health. Additionally, therapists can guide women in building social support networks, accessing community resources, and fostering self-care practices. By providing gender-specific support, therapists can play a crucial role in promoting the psychological well-being of women during the perinatal period.
Eating Disorders
Prevalence of eating disorders in women
Eating disorders are more prevalent in women, and they can have severe physical and psychological consequences. Society’s emphasis on thinness and beauty can contribute to the development of eating disorders, such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorder. These disorders often stem from complex interactions between genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Early intervention and specialized therapeutic approaches are essential in addressing eating disorders in women.
Addressing gender-specific factors in eating disorder treatment
Eating disorder treatment must consider gender-specific factors that contribute to the development and maintenance of these disorders in women. Therapists can explore societal influences, body image concerns, and the impact of cultural norms to develop a comprehensive treatment plan. Addressing gender-specific factors may involve challenging internalized beliefs, developing body acceptance, and promoting a healthy relationship with food and exercise. Therapeutic interventions may also address co-occurring mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety, to facilitate recovery.
Therapeutic approaches to promote recovery in women
Various therapeutic approaches can be effective in promoting recovery from eating disorders in women. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) have shown promising results in treating eating disorders by addressing distorted thoughts, emotions, and behaviors related to food and body image. Family therapy can also play a significant role in supporting women’s recovery, as it involves the whole family in the treatment process. Additionally, therapists can employ holistic approaches that focus on self-compassion, mindfulness, and promoting a balanced lifestyle to support women’s long-term recovery.
Psychological Disorders
Gender differences in the presentation of psychological disorders
Psychological disorders can present differently in women compared to men. For example, women tend to experience higher rates of depression and anxiety disorders. Biological factors, such as hormonal fluctuations and reproductive events, can contribute to these gender differences. Understanding the unique manifestations of psychological disorders in women is crucial for providing accurate diagnoses and effective treatment.
Effective therapies for gender-specific psychological disorders
Women may benefit from therapies that specifically address gender-specific psychological disorders. Therapists may integrate evidence-based approaches such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), or Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) depending on the specific disorder being treated. These therapeutic modalities can help women develop coping strategies, challenge distorted thoughts and beliefs, and promote emotional regulation. By tailoring treatment to address the unique challenges faced by women, therapy can play a significant role in facilitating recovery and improving overall well-being.
Overcoming barriers to mental healthcare for women
Women often face barriers to accessing mental healthcare, including financial constraints, lack of time, societal stigmas, and caregiving responsibilities. Overcoming these barriers is essential to ensure women have equal access to mental health support. Therapists can offer flexible scheduling options, utilize teletherapy platforms, and work with women to identify financial assistance programs or alternative resources. By fostering inclusivity and providing accessible mental healthcare options, therapists can help overcome the barriers that prevent many women from seeking support.
Cultural and Intersectional Considerations
Understanding the impact of culture and intersectionality on therapy
Culture and intersectionality significantly influence women’s experiences and should be considered in therapy. Women from diverse backgrounds may face additional challenges and unique barriers to treatment due to cultural norms, language barriers, discrimination, or marginalization. Therapists must approach therapy with cultural humility and sensitivity, acknowledging and respecting the intersecting identities and experiences of each individual.
Addressing gender-specific therapy needs of women from diverse backgrounds
To effectively address the therapy needs of women from diverse backgrounds, therapists must take an intersectional approach. This approach recognizes the interconnectedness of social identities, such as race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and sexual orientation, and their impact on mental health. Therapists can promote inclusivity by creating a culturally affirming environment, using interpreter services when needed, and continually educating themselves about diverse cultural practices and belief systems.
Inclusive and culturally sensitive therapeutic approaches for women
Therapists can adopt inclusive and culturally sensitive therapeutic approaches for women from diverse backgrounds. This may involve using culturally adapted evidence-based therapies, incorporating traditional healing practices, and tailoring interventions to align with individual beliefs and values. Collaborative goal-setting and mutual respect between therapist and client contribute to a therapeutic alliance built on trust and understanding. By embracing a person-centered approach, therapists can empower women from diverse backgrounds to explore their experiences and work towards their mental health goals.
In conclusion, gender-specific approaches to therapy for women have proven to be effective in addressing a variety of mental health concerns. From body image and self-esteem to trauma and abuse, relationships and intimacy, motherhood and parenting, career and work-life balance, sexual health and reproductive issues, perinatal mental health, eating disorders, psychological disorders, and cultural considerations – therapists who specialize in working with women can provide tailored support to promote women’s mental health and overall well-being. By recognizing the unique challenges faced by women and offering gender-specific therapeutic strategies, therapists can empower women to cultivate resilience, self-acceptance, and fulfillment in various aspects of their lives.